The Legal Requirements For Pay Stubs: A State-By-State Breakdown
In the current world, every employer wants to stay on the right side of the law. Of course, falling on the wrong side can be expensive. One of the major issues employers face is payroll compliance.
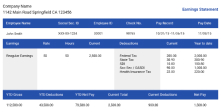
Each time workers are paid, they usually get a statement showing how their wages were determined. This document is referred to as a pay stub, paycheck stub, or wage statement.
It is useful both to employers and employees. However, the requirements relating to these documents are not uniform across all jurisdictions.
In this article, we’ll explain the legal requirements for pay stubs for both employers and employees.
What Are Pay Stubs?
A pay stub is typically attached to an employee's paycheck. It provides important details of the employee’s remuneration for a particular period. Pay stubs have several important uses for employers and employees.
For employers, it is easier to control the payroll overhead costs and determine the total payroll expenses. It helps to ensure compliance with tax regulations. They also offer evidence that can be useful to prevent or settle an employee compensation dispute.
To the employees, the pay stubs assist them in planning and checking whether they have been right. Pay stubs are also important as they serve as proof of income. Employees need this when applying for loans, apartments, grants, or government entitlements.
Besides serving such practical uses, pay stubs have other legal uses as well. They offer proof of the employment relationship. They can be useful in case of a disagreement concerning wages, working hours, or deductions.
The Legal Requirements for Pay Stubs at the Federal Level
Interestingly, there are no federal legal requirements for pay stubs. Federal law does not mandate employers to offer pay stubs to employees. The FLSA outlines provisions for minimum wage, overtime pay, and record-keeping. However, the law does not require companies to issue pay stubs.
Nevertheless, the FLSA mandates that employers keep their employees’ records. This includes records of wages, hours worked, and other working conditions. These records must be kept for not less than three years. It must be made available to the Department of Labor upon request.
Although the FLSA does not mandate pay stubs, employers need to have means of keeping payroll data adequately. This requirement indirectly imposes the usage of pay stubs or similar documents. That is despite the lack of a direct requirement.
Categories of State Pay Stub Laws
Since federal law does not mandate them, every state has its own regulations. The conditions set by state laws can be grouped into several subcategories:
Access States
Currently, twenty-six states mandate employers to allow their employees to access their pay information. However, they don’t prescribe the method through which the information is presented. In these “access states,” the employers can offer both electronic and paper pay stubs. It’s fine as long as employees have easy access to it.
In such states, most employers provide some form of secure online pay stub access. Employees can sign in, view, and download their pay information. These states include:
Alaska
Arizona
Idaho
Illinois
Indiana
Kansas
Kentucky
Maryland
Michigan
Missouri
Montana
Nebraska
Nevada
New Hampshire
New Jersey
New York
North Dakota
Oklahoma
Pennsylvania
Rhode Island
South Carolina
Utah
Virginia
West Virginia
Wisconsin
Wyoming
Access/Print States
Eleven states have more rigid laws on access. They demand that employers must grant employees access to their pay details. But they also make it compulsory to give them a print copy.
These “access/print states” allow the use of the electronic pay stub. However, there has to be an option to generate a physical stub as well. Here, employers can adopt electronic pay systems. Employees must still have an easy mode of printing them out easily if need be. The access/print states include:
California
Colorado
Connecticut
Iowa
Maine
Massachusetts
New Mexico
North Carolina
Texas
Vermont
Washington
Opt-In and Opt-Out States
Some states also have provisions regarding the formatting of pay stubs based on employee preference.
The state of Hawaii is classified as an "opt-in state." This means that the employer must first obtain permission from employees before issuing electronic pay stubs. If consent is not obtained, then employers are required to issue physical pay stubs.
Delaware, Minnesota, and Oregon introduced the "opt-out policy." This allows employers to adopt electronic pay stubs. However, employees still have the right to opt-out and demand a paper pay stub.
No Requirement States
Some states have no pay stub laws defining the kind of records that employers are obliged to give to employees. So, employers are free to decide whether or not to give details of pay to their employees.
Nevertheless, most employers continue to prepare pay stubs as a measure of courtesy. They also do it in a bid to show compliance with other pay requirements. These states are:
Alabama
Arkansas
Florida
Georgia
Louisiana
Mississippi
Ohio
South Dakota
Tennessee
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Lack of adherence to state pay stub laws has some adverse implications in the following ways:
Financial penalties
More often than not, the penalty businesses get is a financial one. In California, for example, first-time offenders will be fined $5. Repeat offenders may be fined $100 per employee for each pay period. The maximum is $4000 per employee.
Audits
Non-compliance can also lead to audits from the Department of Labor or the Internal Revenue Service. This will require employers to present their payroll compliance information and more. In most cases, this comes with exposing other compliance faults.
Lawsuits
The employer is also at risk of being taken to court by employees who didn’t receive their pay stubs. This further invites penalties, attorneys' fees, and compensation costs.
Business Setbacks
Apart from these legal repercussions, the business also suffers setbacks. Non-compliance can make it difficult for an employer to attract and retain competent staff. It could even lead to business shutdowns or ceased operations. This may be due to fines, legal consequences, or loss of reputation. It’s most likely when the violation of the law is compounded with other labor law breaches.
To Sum It Up
To reiterate, it is not part of federal pay stub laws to provide the document to employees. However, most states have laid down laws and regulations to guide this. This protects the relationship between employers and employees when providing this information. Employers and employees have to ensure they understand these legal requirements for pay stubs. This helps them produce proper documents and avoid any payroll compliance pitfalls.
Ensure compliance and transparency with our pay stub creator. Our platform allows businesses to generate accurate, legally compliant pay stubs effortlessly. It doesn’t matter whether you're an employer or an employee. Having detailed payroll records is essential. Visit today and simplify your payroll process!
 Our customer support is available 24/7:
Our customer support is available 24/7: